Orthodontic Appliances
- Bands
- Bonding
- Bracket
- Cephalometric X-ray
- Chain/Powerchain
- Consultation
- Debonding
- Elastic (Rubber Band)
- Extractions
- Fixed Retainer
- Impressions
- Interceptive Treatment
- Interproximal Reduction (IPR)
- Ligation
- Mouthguard
- Oral Hygiene
- Orthodontic Adjustment
- Orthodontic Records
- Palatal
- Panoramic X-ray
- Retainer
- Separator (Spacer)
- Surgery
- Two-Phase Treatment
- Wax

Bands
Bands are metal tooth rings that go around the back molars and serve as anchors for the braces. They have hooks on them so that elastics can be worn.

Bonding
The process of attaching brackets to your teeth using a special safe adhesive.

Bracket
Brackets are the small metal or ceramic modules that are attached to each tooth. They serve as guides to move the teeth and hold the archwire in place.

Cephalometric X-ray
An x-ray of the head that shows if your teeth are aligned and growing properly within the jaws.
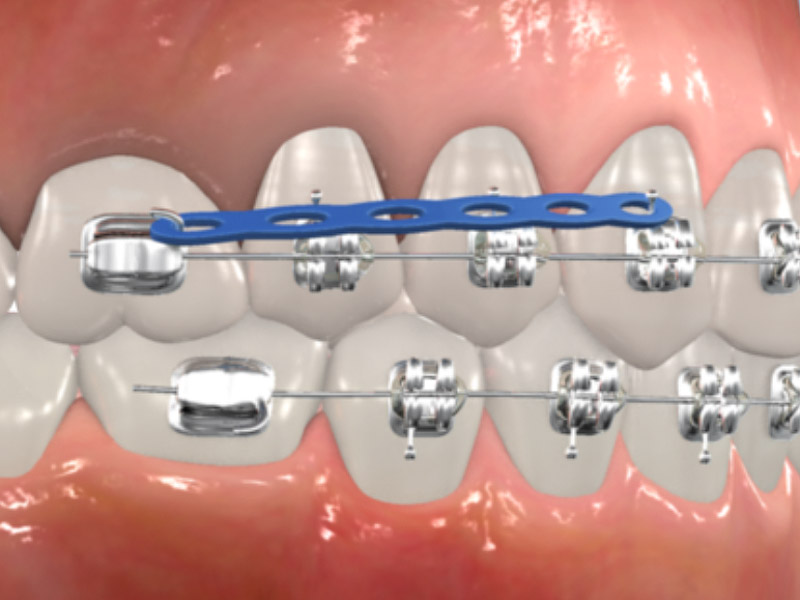
Chain/Powerchain
A stretchable elastic chain that connects on the archwire, usually used to close spaces between the teeth.

Consultation
A meeting with your orthodontist where your treatment plan is discussed.

Debonding
The process of removing cemented orthodontic brackets from your teeth.
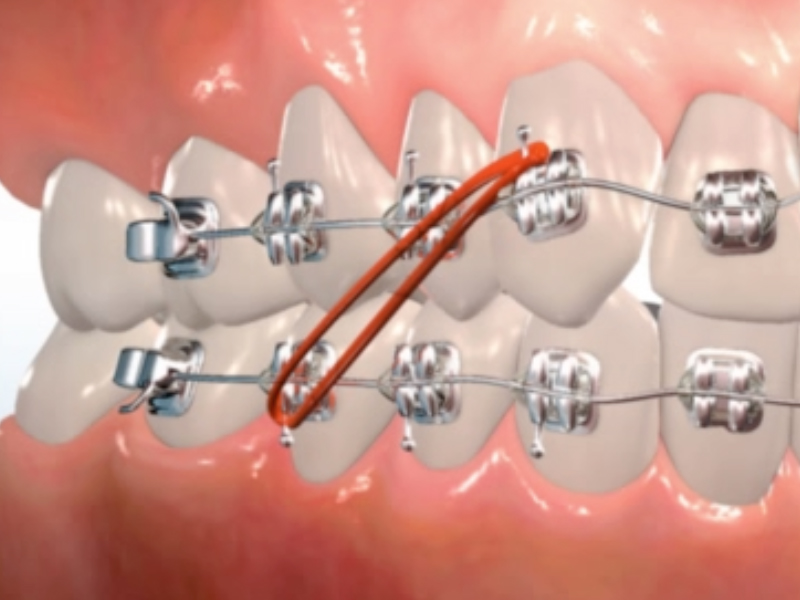
Elastic (Rubber Band)
A small rubber band that is hooked between different points on your appliance to provide gentle, continuous pressure to move your teeth and/or jaws to their new positions. We offer regular or neon colors.

Extractions
Extractions of impacted or problematic teeth to make space for orthodontic treatment.

Fixed Retainer
Fixed retainers consist of a metal wire bonded to the back of the teeth. Fixed retainers can stay in place indefinitely.

Impressions
The first step in making a model of your teeth. You bite into a container filled with a rubber-type material. That material hardens to produce a mold of your teeth.

Interceptive Treatment
Orthodontic treatment that is usually done between the ages of 7 and 10. The objective of interceptive or early orthodontic treatment is to provide orthopedic intervention, so that later orthodontic treatment is less complex.

Interproximal Reduction (IPR)
Interproximal reduction (IPR) is the removal of small amounts of outer enamel tooth surface between two adjacent teeth. It is a means to acquire additional space to create ideal tooth alignment. Alternative names include: slenderizing, stripping, enamel reduction, and reproximation.

Ligation
The process of attaching an archwire to the brackets on your teeth.

Mouthguard
A device that protects your mouth from injury when you participate in sports or rigorous activities.

Oral Hygiene
Effective brushing and flossing is one of the most critical actions needed from patients during braces. Regular visits to the general dentist for examination and cleaning are also essential. The results of inadequate oral hygiene include decalcification (white spots/marks), gingivitis (inflammation of the gums), and periodontal disease (inflammation leading to bone loss).
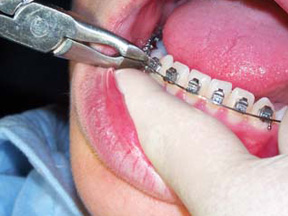
Orthodontic Adjustment
An evaluation of your progress where your wires may be changed to keep your treatment on track and moving forward.

Orthodontic Records
These records, which include cephalometric and panoramic x-rays, digital photos and study models, help your orthodontist determine what treatment needs to be done.

Palatal
Adjacent to the roof of the mouth.

Panoramic X-ray
An X-ray taken by a machine that rotates around your head to give your orthodontist a picture of your teeth, jaws, and other important information.

Retainer
An appliance that is worn after your braces are removed. The retainer attaches to your upper and/or lower teeth to hold them in place. Some retainers are removable, and others are bonded to the teeth.

Separator (Spacer)
A small rubber ring that creates space between your teeth before the bands are attached.

Surgery
Orthognathic surgery is surgery performed on the bones of the jaws to change their positions. It may be considered for functional, cosmetic, or health reasons. It is surgery commonly performed on the jaws in conjunction with orthodontic treatment, which straightens the teeth.

Two-Phase Treatment
Two phase orthodontic treatment is a very specialized process that encompasses tooth straightening and physical, facial changes. The major advantage of a two-phase treatment is to maximize the opportunity to accomplish the ideal healthy, functional, and aesthetic result that will remain stable throughout your life.

Wax
A clear wax used to prevent your braces from irritating your lips or cheeks when your braces are first put on, or as needed. Wax works best when the irritating area is dried well first and then, embedded totally within the pea-sized or grape-sized ball of wax.
Bands

Bands are metal tooth rings that go around the back molars and serve as anchors for the braces. They have hooks on them so that elastics can be worn.
Bonding

The process of attaching brackets to your teeth using a special safe adhesive.
Bracket

Brackets are the small metal or ceramic modules that are attached to each tooth. They serve as guides to move the teeth and hold the archwire in place.
Cephalometric X-ray

An x-ray of the head that shows if your teeth are aligned and growing properly within the jaws.
Chain/Powerchain

A stretchable elastic chain that connects on the archwire, usually used to close spaces between the teeth.
Consultation

A meeting with your orthodontist where your treatment plan is discussed.
Debonding

The process of removing cemented orthodontic brackets from your teeth.
Elastic (Rubber Band)

A small rubber band that is hooked between different points on your appliance to provide gentle, continuous pressure to move your teeth and/or jaws to their new positions. We offer regular or neon colors.
Extractions

Extractions of impacted or problematic teeth to make space for orthodontic treatment.
Fixed Retainer

Fixed retainers consist of a metal wire bonded to the back of the teeth. Fixed retainers can stay in place indefinitely.
Impressions

The first step in making a model of your teeth. You bite into a container filled with a rubber-type material. That material hardens to produce a mold of your teeth.
Interceptive Treatment

Orthodontic treatment that is usually done between the ages of 7 and 10. The objective of interceptive or early orthodontic treatment is to provide orthopedic intervention, so that later orthodontic treatment is less complex.
Interproximal Reduction (IPR)

Interproximal reduction (IPR) is the removal of small amounts of outer enamel tooth surface between two adjacent teeth. It is a means to acquire additional space to create ideal tooth alignment. Alternative names include: slenderizing, stripping, enamel reduction, and reproximation.
Ligation

The process of attaching an archwire to the brackets on your teeth.
Mouthguard

A device that protects your mouth from injury when you participate in sports or rigorous activities.
Oral Hygiene

Effective brushing and flossing is one of the most critical actions needed from patients during braces. Regular visits to the general dentist for examination and cleaning are also essential. The results of inadequate oral hygiene include decalcification (white spots/marks), gingivitis (inflammation of the gums), and periodontal disease (inflammation leading to bone loss).
Orthodontic Adjustment

An evaluation of your progress where your wires may be changed to keep your treatment on track and moving forward.
Orthodontic Records

These records, which include cephalometric and panoramic x-rays, digital photos and study models, help your orthodontist determine what treatment needs to be done.
Palatal

Adjacent to the roof of the mouth.
Panoramic X-ray

An X-ray taken by a machine that rotates around your head to give your orthodontist a picture of your teeth, jaws, and other important information.
Retainer

An appliance that is worn after your braces are removed. The retainer attaches to your upper and/or lower teeth to hold them in place. Some retainers are removable, and others are bonded to the teeth.
Separator (Spacer)

A small rubber ring that creates space between your teeth before the bands are attached.
Surgery

Orthognathic surgery is surgery performed on the bones of the jaws to change their positions. It may be considered for functional, cosmetic, or health reasons. It is surgery commonly performed on the jaws in conjunction with orthodontic treatment, which straightens the teeth.
Two-Phase Treatment

Two phase orthodontic treatment is a very specialized process that encompasses tooth straightening and physical, facial changes. The major advantage of a two-phase treatment is to maximize the opportunity to accomplish the ideal healthy, functional, and aesthetic result that will remain stable throughout your life.
Wax

A clear wax used to prevent your braces from irritating your lips or cheeks when your braces are first put on, or as needed. Wax works best when the irritating area is dried well first and then, embedded totally within the pea-sized or grape-sized ball of wax.











